Sun and Over Exposure to Melanated Skin

Sun damage can affect people of all skin types, including those with darker skin tones, although the risk and presentation may differ compared to individuals with lighter skin. Here are some key points to consider:
-
Sunburn: People with darker skin tones have more melanin, which provides some natural protection against the harmful effects of UV radiation. This means they are less likely to experience sunburn compared to individuals with lighter skin. However, it's important to note that sunburn can still occur in people with dark skin, especially if they are exposed to intense or prolonged sun.
-
Hyperpigmentation: Darker-skinned individuals are more prone to a condition called post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH). This occurs when the skin produces extra melanin in response to injury, including sunburn. PIH can lead to the development of dark spots or patches on the skin that may take months or even years to fade.
-
Skin Cancer: While people with darker skin have a lower risk of skin cancer compared to those with lighter skin, they are not immune to it. Skin cancer can still occur in individuals with all skin types, so it's essential for everyone, regardless of their skin color, to protect their skin from excessive sun exposure and regularly check for unusual moles or skin changes.
-
Aging Effects: Sun damage can accelerate the aging process of the skin, leading to the development of fine lines, wrinkles, and age spots. These effects can be seen in people of all skin tones, including those with darker skin.
-
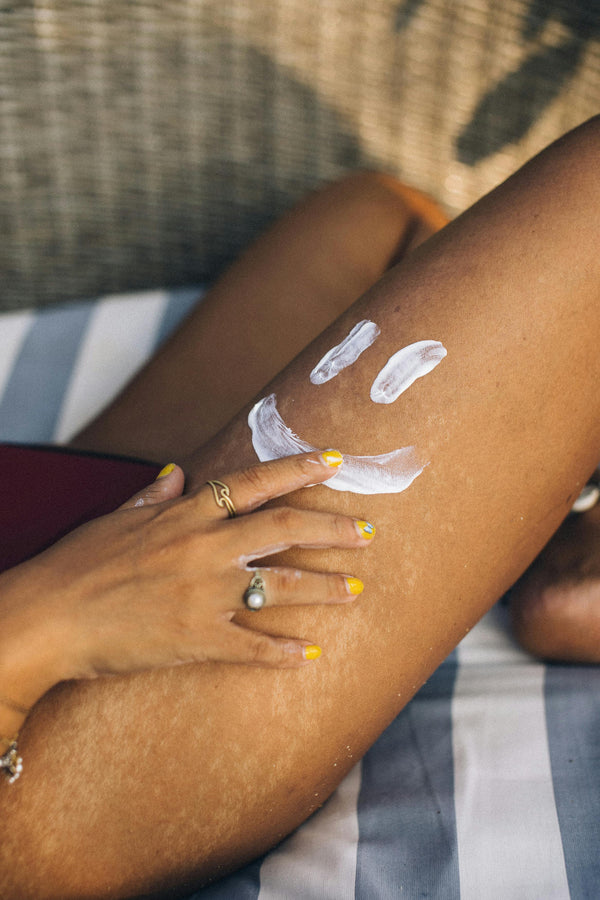
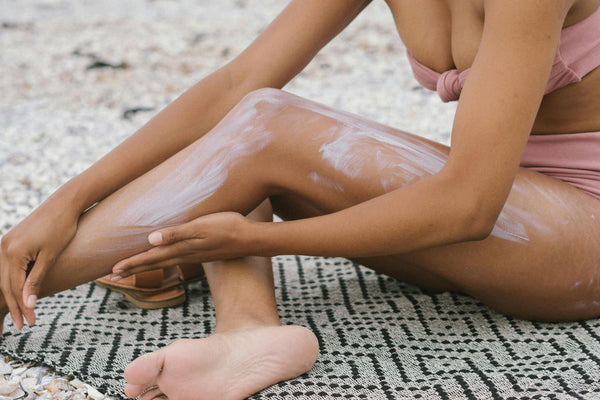
Sun Protection: To minimize the risk of sun damage, it's important for individuals with darker skin to use sunscreen with broad-spectrum protection, wear protective clothing (such as wide-brimmed hats and long sleeves), and seek shade during peak sun hours. Using sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher and reapplying it regularly is crucial, as is applying it to all exposed areas, including the face and neck.
-
Consultation with a Dermatologist: If you have concerns about sun damage or want to address specific skin issues related to sun exposure, consider consulting a dermatologist. They can provide personalized advice and recommend appropriate skincare products and treatments.
In summary, while individuals with darker skin have some inherent protection against sunburn, they are still susceptible to sun damage, including hyperpigmentation, skin cancer, and premature aging. Sun protection measures are essential for maintaining healthy skin regardless of one's skin color.